Writing a script#
There are currently 3 types of scripts:
- Javascript scripts (*.js)
- non-visual QML scripts (*.qml)
- visual QML scripts (*.qml)
If the first line is a comment, it will be used as the script description.
If you need to know more about QML, follow this link: https://doc.qt.io/qt-6/qmlapplications.html
Both Javascript and QML scripts use the same API, see the Knut API reference.
For more advanced use cases, take a look at: Syntax tree queries using Tree-sitter
Javascript script#
Javascript scripts must contain a main function, the entry point for the script:
// Script description
function main() {
message.log("Hello World!")
}
Non-visual QML scripts#
QML scripts are written using the Script item.
// Script description
import Knut
Script {
function init() {
// called at started
message.log("Hello World!")
}
// ...
}
The init() function in the root item (visual or not) will automatically be called at startup.
Visual QML scripts#
To create a visual script, you can use the ScriptDialog item. Such a script requires a second ui file, with the same name and in the same folder as the qml file.
For example, here is a small ui file named my-script.ui
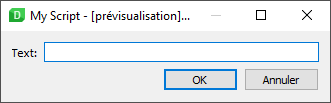
The script using this ui file will be called my-script.qml:
// Script description
import Knut
ScriptDialog {
function init() {
// called at started
data.lineEdit = "Hello World!"
}
onAccepted: {
message.log(data.lineEdit)
close()
}
}
The QLineEdit (named lineEdit) in the ui file is accessed both in reading and writing via data.lineEdit.
Note that the init() function in the root item (visual or not) will automatically be called at startup.
In a visual script, the init() function usually should not start the code transformation, but should wait for the dialog to be accepted, or a button to be clicked, etc.
Supported widgets#
Here is the list of supported widgets for your dialogs, and how to access them from the QML script.
| Widget | API used |
|---|---|
QDialogButtonBox |
Click notification via the onAccepted and onRejected signal handlers |
QPushButton |
Click notification via the onClikced(name) signal handler, with name being the objectName of the button |
QToolButton |
Click notification via the onClikced(name) signal handler, with name being the objectName of the button |
QLineEdit |
Text via data.objectName |
QCheckBox |
Check value via data.objectName |
QRadioButton |
Check value via data.objectName |
QSpinBox |
Value (int) via data.objectName |
QDoubleSpinBox |
Value (double) via data.objectName |
QComboBox |
Text via data.objectName, the list of values is available via data.objectNameModel |
A note about QComboBox: if the combo box is editable, it will use the list of values as input data for completion.
Alternative: using QtQuick#
You can also use directly QtQuick and QtQcuick.Controls if you want, for example a script with a button printing "Hello World!" in the log:
// Script description
import QtQuick
import QtQuick.Controls
import QtQuick.Layouts
import Knut
ApplicationWindow {
width: 300
height: 300
ColumnLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
Button {
Layout.fillWidth: true
text: "Log"
onClicked: message.log("Hello World!")
}
}
}