Command Line Interface#
Using command line options#
You can start knut by passing directly some options to the command line, using it in a headless way:
knut [option] [project]
The project is the directory containing the source code you want to work on. All available options are documented here:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
-r, --run <file> |
Runs given script <file> then exit |
-t, --test <file> |
Tests given script <file> then exit |
-i, --input <file> |
Opens document <file> on startup |
-l, --line <line> |
Sets the line in the current file, if any |
-c, --column <column> |
Sets the column in the current file, if any |
| --gui-run | Opens the run script dialog |
| --gui-settings | Opens the settings dialog |
| --json-list | Returns the list of all available scripts as a JSON file |
| --json-settings | Returns the settings as a JSON file |
Note: the json options are mainly used for integration with 3rd party, not meant to be used by user directly.
Without any options, knut will start the user interface.
IDE integration#
Using the command line interface, one can integrate with existing IDE.
Qt Creator#
To add knut to Qt Creator, go to the menu Tools>External>Configure..., create a new tool, and fill the different fields for a new tool.
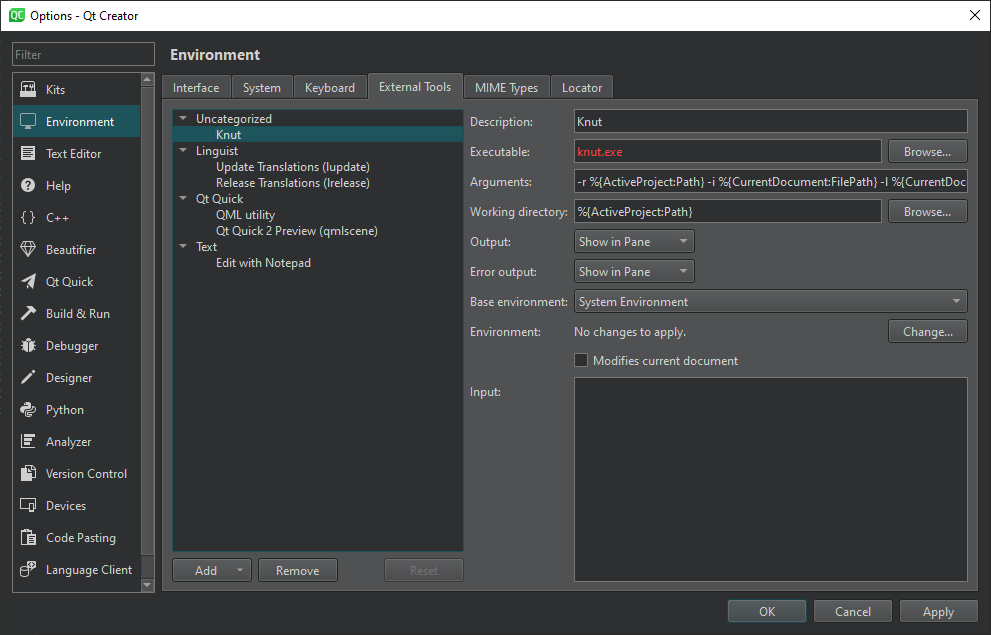
Particularly:
- in Arguments, you can use different variables, like:
--root %{ActiveProject:NativePath}--input %{CurrentDocument:FilePath}--line %{CurrentDocument:Row}--column %{CurrentDocument:Column}
- in Working directory:
%{ActiveProject:NativePath}
For example, to open the knut user interface using the same project and same file as Qt Creator, you will pass in Arguments:
--input %{CurrentDocument:FilePath} --line %{CurrentDocument:Row} --column %{CurrentDocument:Column} %{ActiveProject:NativePath}